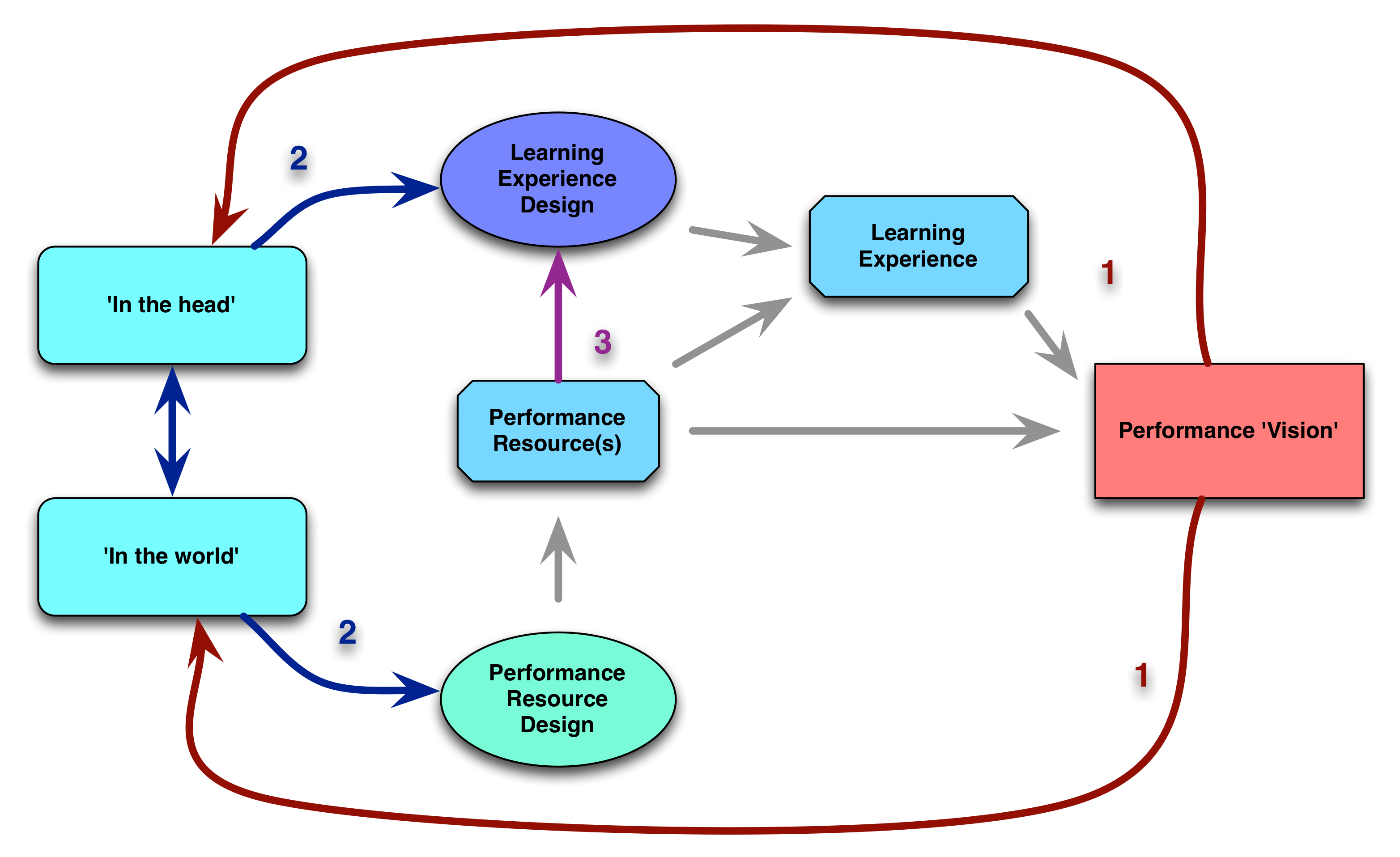
Don Norman (disclaimer, my PhD advisor and mentor) has had a string of important books, starting with his stellar Design of Everyday Things (tops my ‘recommended books’ list for designers). His latest, Living with Complexity, is not as landmark a book as that, but it has some very astute thinking to present.
The book, as the title implies, is largely about how complexity isn’t bad, it’s necessary, and the real issue is about designing to manage it. We want powerful systems to accomplish meaningful goals, and he makes the case that this naturally requires complexity, either at the front end or at the back end. Complexity at the front end offers powerful choice at the tradeoff of comprehensibility, which we often want. Complexity at the back end can seem like magic, but offers more opportunity for things to go wrong catastrophically.
Good design is naturally the solution. He suggests that good design makes complexity usable, and bad design makes complexity frustrating. And he makes a strong point that it’s now about services.
He goes beyond product design in detailing how you really aren’t designing just a product, but an experience, and that it takes a system to create an experience. Using Apple’s iPod, he points out how simplifying the purchasing (backend: lining up publishers to allow downloading individual titles for a simple fee) and downloading music (instead of converting files and storing in special folders) made a device that could carry a lot of music in a small package.
He goes deeper into service design, using the examples of waiting in lines (I now know why immigration in SFO can be so frustrating!). He finally gets to coverage of recommendations for improvements, including signifying (making affordances perceivable), checklists, and job aids (over courses). His focus is on tapping into how our minds work, and aligning tools with them. He covers both sides, including what designers should do differently, and what ‘consumers’ can do. He also covers some of the mismatches between design and consumers, going beyond the design to the overall system.
Overall, while seemingly not as well structured as previous books, this book offers some advanced thinking into design that will benefit those looking to take a bigger picture. Feeling more like a collection rather than a coherent narrative, each of the elements is related and there are important insights in each section. Recommended for the advanced designer.
 An increasing number of organisations, independent of size, nature or location, will acknowledge that their traditional training and development models and processes are failing to live up to the expectations of their leaders and workforce in a dynamic and global marketplace. Some will take steps to use their financial and people resources and exploit new ways of working and learning. Others will be hamstrung with outdated skills, tools and technologies, and will be too slow to adapt. A confluence of technology and improved connectivity, increasing pressures for rapid solutions and better customer service, and demands for higher performance, will force the hands of many HRDs and CLOs to refocus from models of ‘extended formal training‘ to place technology-enabled, workplace-focused and leader-led development approaches at the core of their provision. We will move a step or two closer to real-time performance support at the point of need.
An increasing number of organisations, independent of size, nature or location, will acknowledge that their traditional training and development models and processes are failing to live up to the expectations of their leaders and workforce in a dynamic and global marketplace. Some will take steps to use their financial and people resources and exploit new ways of working and learning. Others will be hamstrung with outdated skills, tools and technologies, and will be too slow to adapt. A confluence of technology and improved connectivity, increasing pressures for rapid solutions and better customer service, and demands for higher performance, will force the hands of many HRDs and CLOs to refocus from models of ‘extended formal training‘ to place technology-enabled, workplace-focused and leader-led development approaches at the core of their provision. We will move a step or two closer to real-time performance support at the point of need. We‘ll see an increasing use of mobile, and some organizations will recognize the platform that such devices provide to move the full suite of learning support (specifically performance support and informal learning) out to employees, dissolving the arbitrary boundaries between training and the full spectrum of possibilities. Others will try to cram courses onto phones, and continue to miss the bigger picture, increasing their irrelevance. Further, we‘ll see more examples of the notion of a ‘performance ecosystem‘ of resources aligned around individual needs and responsibilities, instead of organized around the providing silos. We‘ll also see more interactive and engaging examples of experience design, and yet such innovative approaches will continue to be reserved for the foresightful, while most will continue in the hidebound status quo. Finally, we‘ll see small starts in thinking semantic use in technology coupled with sound ethnographic methods to start providing just such smart support, but the efforts will continue to be embryonic.
We‘ll see an increasing use of mobile, and some organizations will recognize the platform that such devices provide to move the full suite of learning support (specifically performance support and informal learning) out to employees, dissolving the arbitrary boundaries between training and the full spectrum of possibilities. Others will try to cram courses onto phones, and continue to miss the bigger picture, increasing their irrelevance. Further, we‘ll see more examples of the notion of a ‘performance ecosystem‘ of resources aligned around individual needs and responsibilities, instead of organized around the providing silos. We‘ll also see more interactive and engaging examples of experience design, and yet such innovative approaches will continue to be reserved for the foresightful, while most will continue in the hidebound status quo. Finally, we‘ll see small starts in thinking semantic use in technology coupled with sound ethnographic methods to start providing just such smart support, but the efforts will continue to be embryonic. People who know nothing about connectivism or collaborative learning will profit from MOOC‘s. Academics and instructional designers will tell anyone who wants to listen just how important formal training is, as it fades in relevance to both learners and businesses.The ITA will keep on questioning the status quo and show how work is learning and learning is the work in the network era – some will listen, many will not.
People who know nothing about connectivism or collaborative learning will profit from MOOC‘s. Academics and instructional designers will tell anyone who wants to listen just how important formal training is, as it fades in relevance to both learners and businesses.The ITA will keep on questioning the status quo and show how work is learning and learning is the work in the network era – some will listen, many will not. Many traditional-thinking organisations will waste a lot of time and energy trying to track social interventions in the hope that they can control and manage “social learningâ€. Whilst those organisations who appreciate that social learning is a natural and continuous part of working, will acknowledge that the most appropriate approach they can take is simply to support it in the workplace – both technologically and in terms of modelling new collaborative behaviours. Meanwhile, we will continue to see individuals and teams bypass IT and T&D departments and solve their learning and performance problems more quickly and easily using their own devices to access online resources, tools and networks.
Many traditional-thinking organisations will waste a lot of time and energy trying to track social interventions in the hope that they can control and manage “social learningâ€. Whilst those organisations who appreciate that social learning is a natural and continuous part of working, will acknowledge that the most appropriate approach they can take is simply to support it in the workplace – both technologically and in terms of modelling new collaborative behaviours. Meanwhile, we will continue to see individuals and teams bypass IT and T&D departments and solve their learning and performance problems more quickly and easily using their own devices to access online resources, tools and networks. 2013 will be a great year. As William Gibson wrote, “The future‘s already here. It‘s just not evenly distributed yet.†The business world will become a bit more complex — and therefore more chaotic and unpredictable. Moore‘s Law and exponential progress will continue to work their magic and speed things up. Learning will continue to converge with work. Increasingly, workers will learn their jobs by doing their jobs. The lessons of motivation (a la Dan Pink) and the importance of treating people like people will sink in. Smart companies will adopt radical management, putting the customer in charge and reorganizing work in small teams. Senior people will recognize that emotions drive people — and there are other emotions in addition to passion. Happy workers are more engaged, more productive, and more fulfilled. What‘s not to like?
2013 will be a great year. As William Gibson wrote, “The future‘s already here. It‘s just not evenly distributed yet.†The business world will become a bit more complex — and therefore more chaotic and unpredictable. Moore‘s Law and exponential progress will continue to work their magic and speed things up. Learning will continue to converge with work. Increasingly, workers will learn their jobs by doing their jobs. The lessons of motivation (a la Dan Pink) and the importance of treating people like people will sink in. Smart companies will adopt radical management, putting the customer in charge and reorganizing work in small teams. Senior people will recognize that emotions drive people — and there are other emotions in addition to passion. Happy workers are more engaged, more productive, and more fulfilled. What‘s not to like?