Eileen Clegg from the Future of Talent Institute (and colleague, we co-wrote the Extremophiles chapter for Creating a Learning Culture) pinged me the other day and asked about my thoughts on the intersection of:
- The new role of managers in the results-oriented work environment (ROWE)
- The topic of blending the Talent and Learning functions in the workplace.
She’d been excited about Cognitive Apprenticeship years ago after hearing me talk about it, and wondered if there was a role to play. I see it as two things: orgs need optimal execution just as the cost of entry: that’s where apprenticeship fits in, but they also need continual innovation. That needs collaboration, and we are still exploring that, though there are some really clear components. Though one of the nice things about cognitive apprenticeship is that it naturally incorporates collaborative learning, and can develop that as it develops understanding of the domain.
I admit I’m a little worried about ROWE from the point of view that Dan Pink picks out in Drive, about how a maniacal focus on results could lead to people doing anything necessary to achieve results. It’s got to be a little more about taking mutual ownership (producer and whoever is ‘setting’ the result) that the result is meeting the org need in a holistic (even ‘wise’ way).
What has to kick in here is a shared belief in a vision/mission that you can get behind, individuals equipped to solve problems collaboratively (what I call big L learning: research, design, experimentation, etc), and tools to hand for working together. You apprentice both in tasks *and* learning, basically, until you’re an expert in your domain are defining what’s new in conjunction with your collaborators.
Expressed by my colleague was a concern that there was a conflict between”(a) supporting someone’s learning and (b) being invested in the success of their work product”. And I would think that the management is NOT directly invested in the product, only in the producer. Helping them be the best they can be and all that. If they’re not producing good output, they either need to develop the person or replace them, which indirectly affects the product. However, this isn’t new for mentors as well: they want their charges to do well, but the most they can do is influence the performer to the best of their ability.
As a component, learners need to develop their PKM/PLN (personal knowledge management, personal learning network). And 21st century skills aren’t taken for granted but identified and developed. In addition, the performance ecosystem, aka workscape – not only formal learning but also performance support, informal learning, and social learning – is the responsibility of the integrated talent/learning functions (which absolutely should be blended). And ‘management’ may move more toward mentorship, or be a partner between someone strategizing across tasks and a talent development function in the organization.
As an extension to my ‘slow learning’ model, I think that the distinction between learning and performing from the point of view of support needs to go away. We can and should be concerned with the current performance and the long-term development of the learner at the same time. Thus, the long term picture is of ongoing apprenticeship towards mutually negotiated and understood goals, both work and personal development.
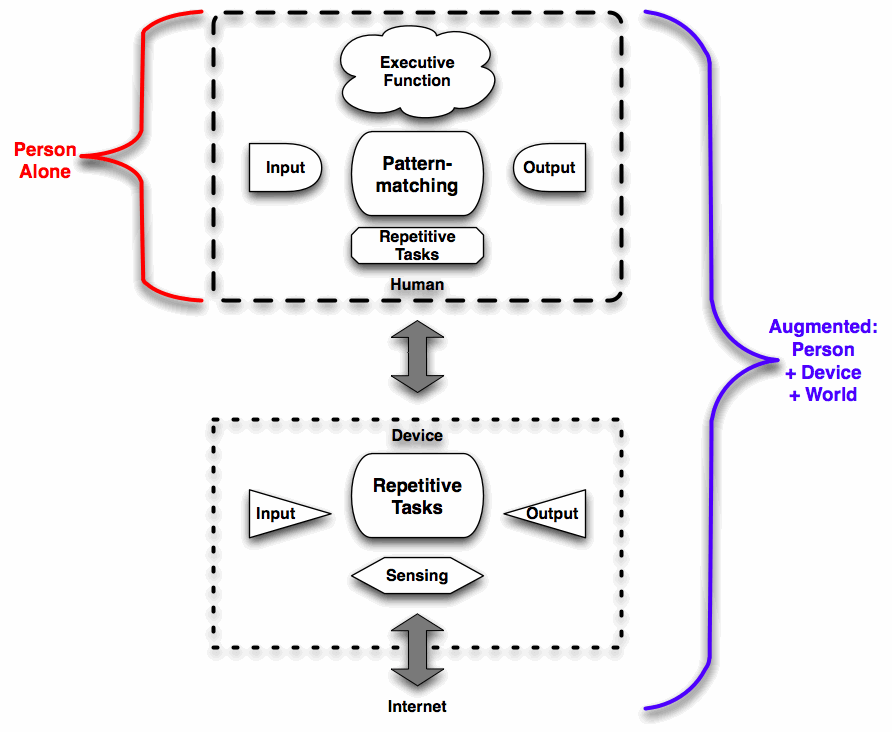
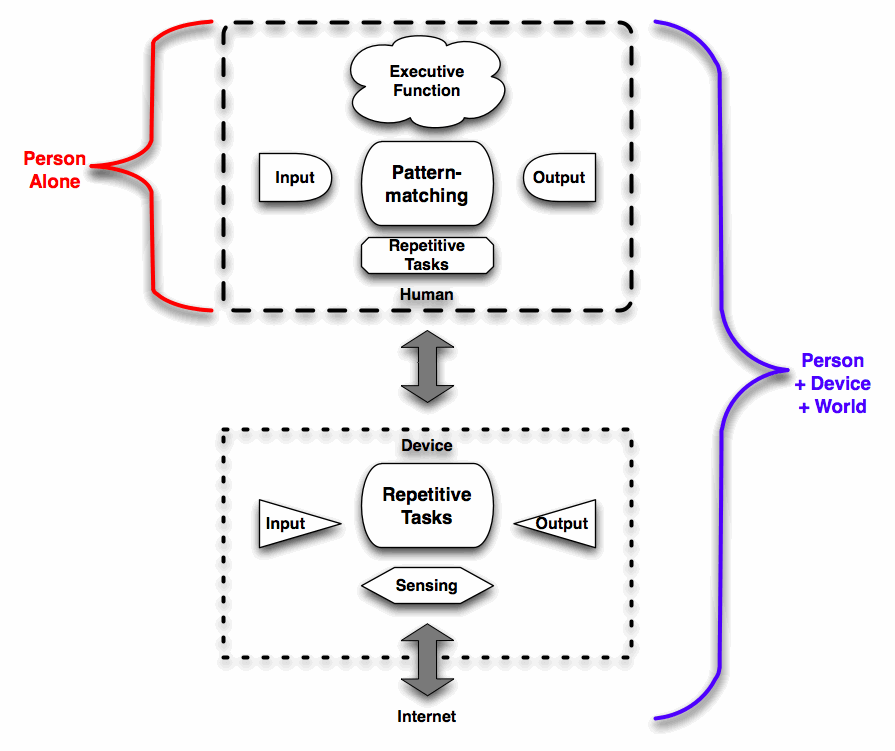 If we look at our human capabilities, we’re very good pattern matchers, but pretty bad at exercising rote performance. So we can identify problems, and strategize about solutions, but when it comes to executing rote tasks, like calculation, we’re slow and error prone. From the point of the view of a problem we’re trying to solve, we’re not as effective as we could be.
If we look at our human capabilities, we’re very good pattern matchers, but pretty bad at exercising rote performance. So we can identify problems, and strategize about solutions, but when it comes to executing rote tasks, like calculation, we’re slow and error prone. From the point of the view of a problem we’re trying to solve, we’re not as effective as we could be.