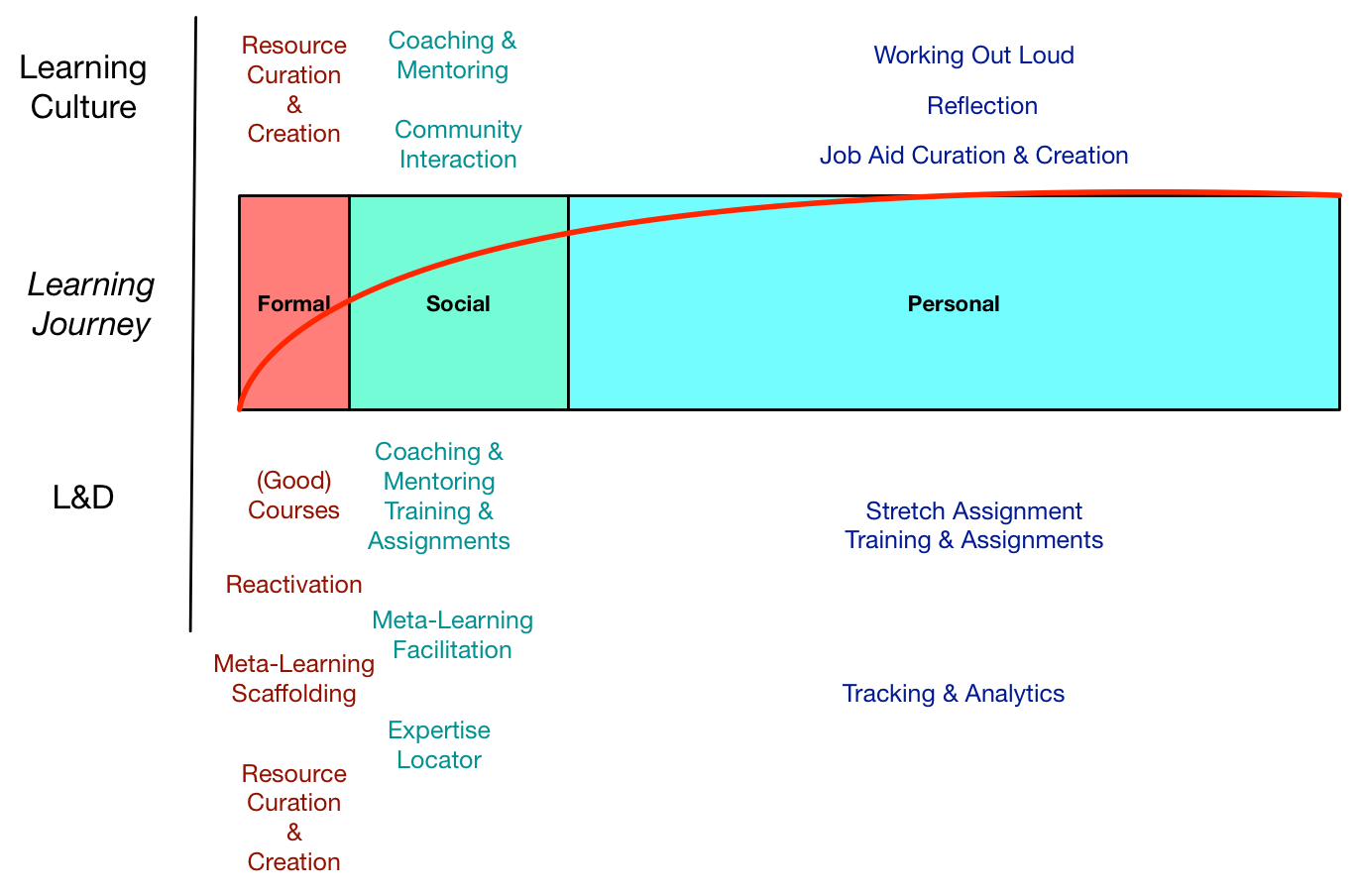
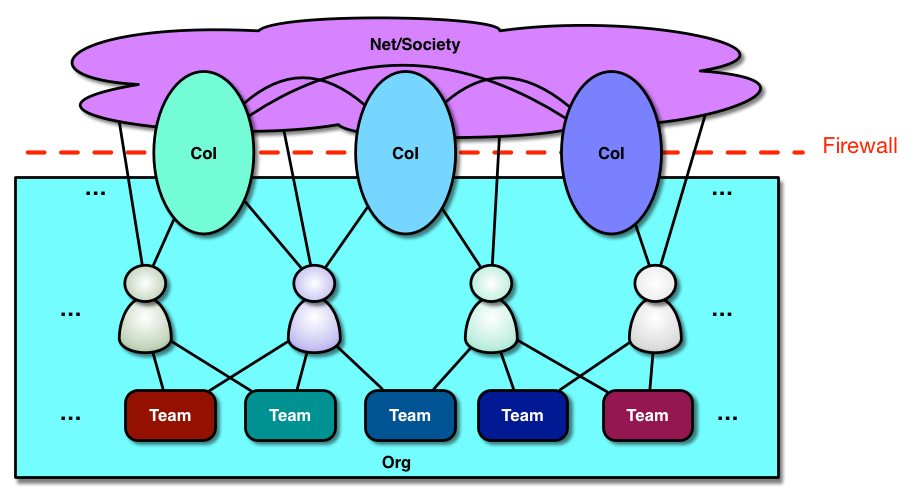
One of the realizations I had in writing the Revolutionize L&D book was how badly we’re out of synch with our brains. I think alignment is a big thing, both from the Coherent Organization perspective of having our flows of information aligned, and in processes that help us move forward in ways that reflect our humanity.
In short, I believe we’re out of alignment with our views on how we think, work, and learn. The old folklore that represents the thinking that still permeates L&D today is based upon outdated models. And we really have to understand these differences if we’re to get better.
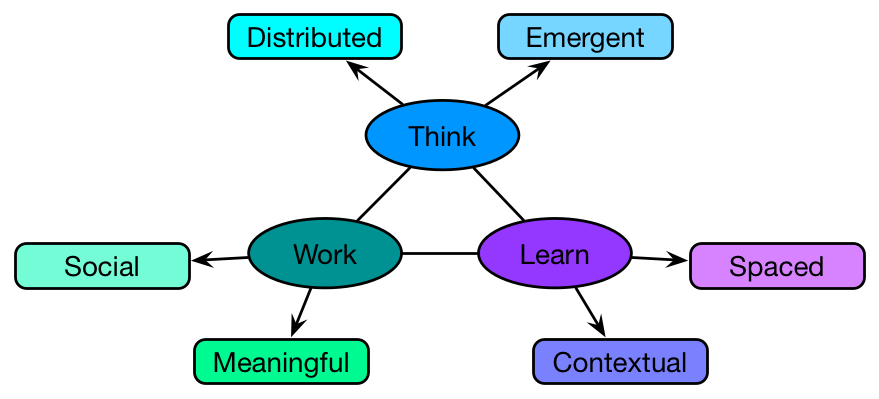 The mistaken belief about thinking is that it’s all done in our head. That is, we keep the knowledge up there, and then when a context comes in we internalize it and make a logical decision and then we act. And what cognitive science says is that this isn’t really the way it works. First, our thinking isn’t all in our heads. We distribute it across representational tools like spreadsheets, documents, and (yes) diagrams. And we don’t make logical decisions without a lot of support or expertise. Instead, we make quick decisions. This means that we should be looking at tools to support thinking, not just trying to put it all in the head. We should be putting as much in the world as we can, and look to scaffold our processes as well.
The mistaken belief about thinking is that it’s all done in our head. That is, we keep the knowledge up there, and then when a context comes in we internalize it and make a logical decision and then we act. And what cognitive science says is that this isn’t really the way it works. First, our thinking isn’t all in our heads. We distribute it across representational tools like spreadsheets, documents, and (yes) diagrams. And we don’t make logical decisions without a lot of support or expertise. Instead, we make quick decisions. This means that we should be looking at tools to support thinking, not just trying to put it all in the head. We should be putting as much in the world as we can, and look to scaffold our processes as well.
It’s also this notion that we go away and come up with the answer, and that the individual productivity is what matters. It turns out that most innovation, problem-solving, etc, gets better results if we do it together. As I often say “the room is smarter than the smartest person in the room if you manage the process right“. Yet, we don’t. And people work better when they understand why what they’re doing is important and they care about it. We should be looking at ways to get people to work together more and better, but instead we still see hierarchical decision making, restrictive cultures, and more.
And, of course, there still persists this model that information dump and knowledge test will lead to new capabilities. That’s a low probability approach. Whereas if you’re serious about learning, you know it’s mostly about spacing contextualized application of that knowledge to solve problems. Instead, we see rapid elearning tools and templates that tart-up quiz questions.
The point being, we aren’t recognizing that which makes us special, and augmenting in ways that bring out the best. We’re really running organizations that aren’t designed for humans. Most of the robotic work should and will get automated, so then when we need to find ways to use people to do the things they’re best at. It should be the learning folks, and if they’re not ready, well, they better figure it out or be left out! So let’s get a jump on it, shall we?