 I ranted a couple of weeks ago about how we need to move out of our complacency and make a positive change. As I sometimes do, I stumbled upon a diagram that characterizes the type of change I think we need to be considering.
I ranted a couple of weeks ago about how we need to move out of our complacency and make a positive change. As I sometimes do, I stumbled upon a diagram that characterizes the type of change I think we need to be considering.
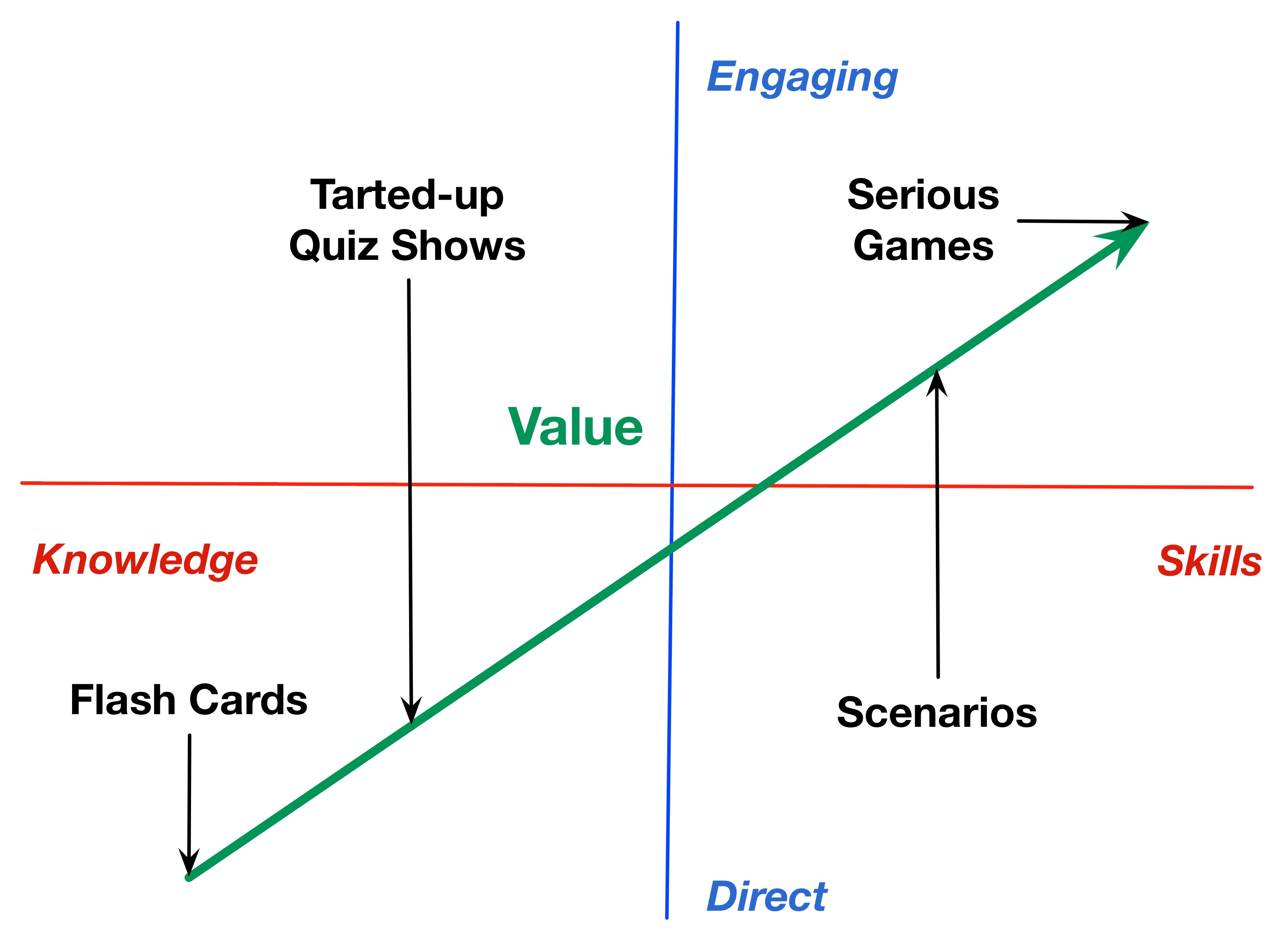
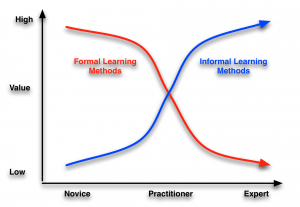
The perspective riffs off of the concept of the relative value of formal versus informal learning methods shift as performers move from novice to expert. (And, as I’ve previously noted, what’s considered in/formal changes depending on if you’re the performer or designer.) And, too often, we tend to restrict our interventions to the formal side, yet there are lots of things we can be doing on the informal side.
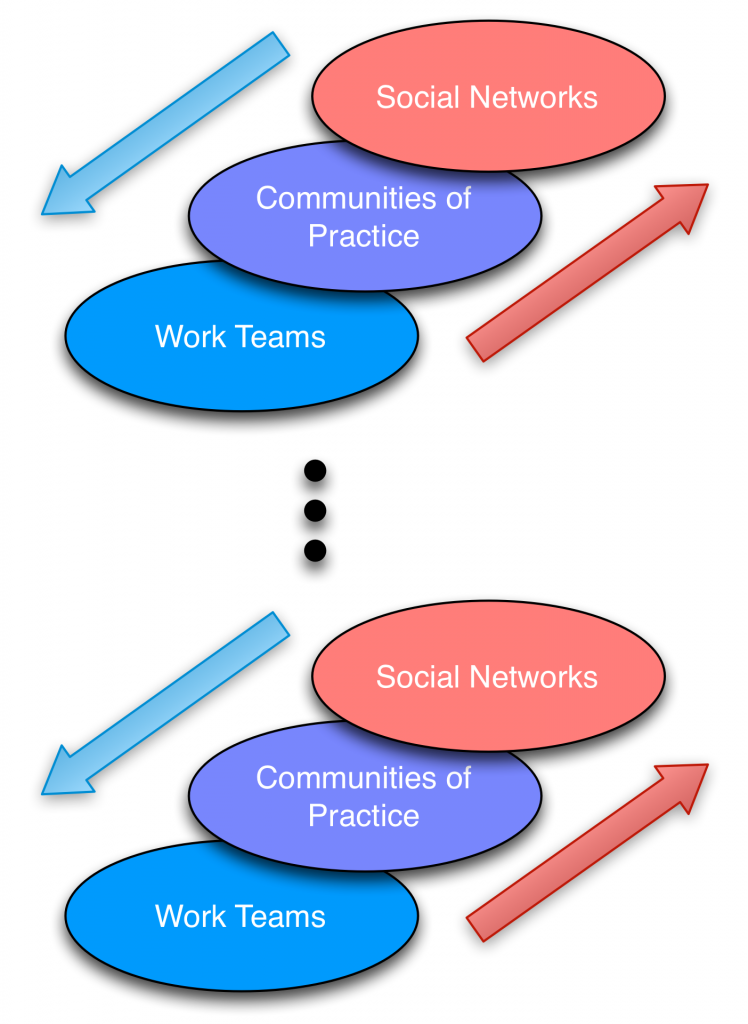
 Largely, however, I see learning and development (L&D) groups as focusing exclusively on novices, or to beginning practitioners, and leaving practitioners and experts on their own. Even if they’re addressing these more advanced audiences, they tend to use the ‘course’ as the vehicle, when it’s not really necessary. These audiences know what they need to know, and just want that useful information, they don’t need the full preparation that novices do. Novices don’t know what they need to know nor why it’s important, so we provide all that in a course model. We can be much more telegraphic to advanced performers, and the value of social networks starts kicking in here too.
Largely, however, I see learning and development (L&D) groups as focusing exclusively on novices, or to beginning practitioners, and leaving practitioners and experts on their own. Even if they’re addressing these more advanced audiences, they tend to use the ‘course’ as the vehicle, when it’s not really necessary. These audiences know what they need to know, and just want that useful information, they don’t need the full preparation that novices do. Novices don’t know what they need to know nor why it’s important, so we provide all that in a course model. We can be much more telegraphic to advanced performers, and the value of social networks starts kicking in here too.
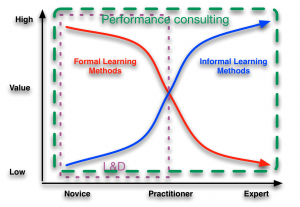
The point I’m trying to make is that we can, and should, take responsibility for the rest of the performers. We can assist their performance, hence the term we’ve been preferring in the Internet Time Alliance: performance consultant. This implies facilitating performance across the organizational roles, top to bottom and from beginner to expert.
I’d like to suggest that L&D groups need to become focused on facilitating organizational performance, which includes but is not limited to training. It’s going to benefit the organization, it’s going to lead to greater strategic contributions and associated value, and it’s an approach that will likely preclude a long slow march to irrelevance and extinction. Better the folks that understand how we learn and perform (and if you don’t, what are you waiting for?) take responsibility than having it devolve by default to business units and/or IT, eh?
#itashare