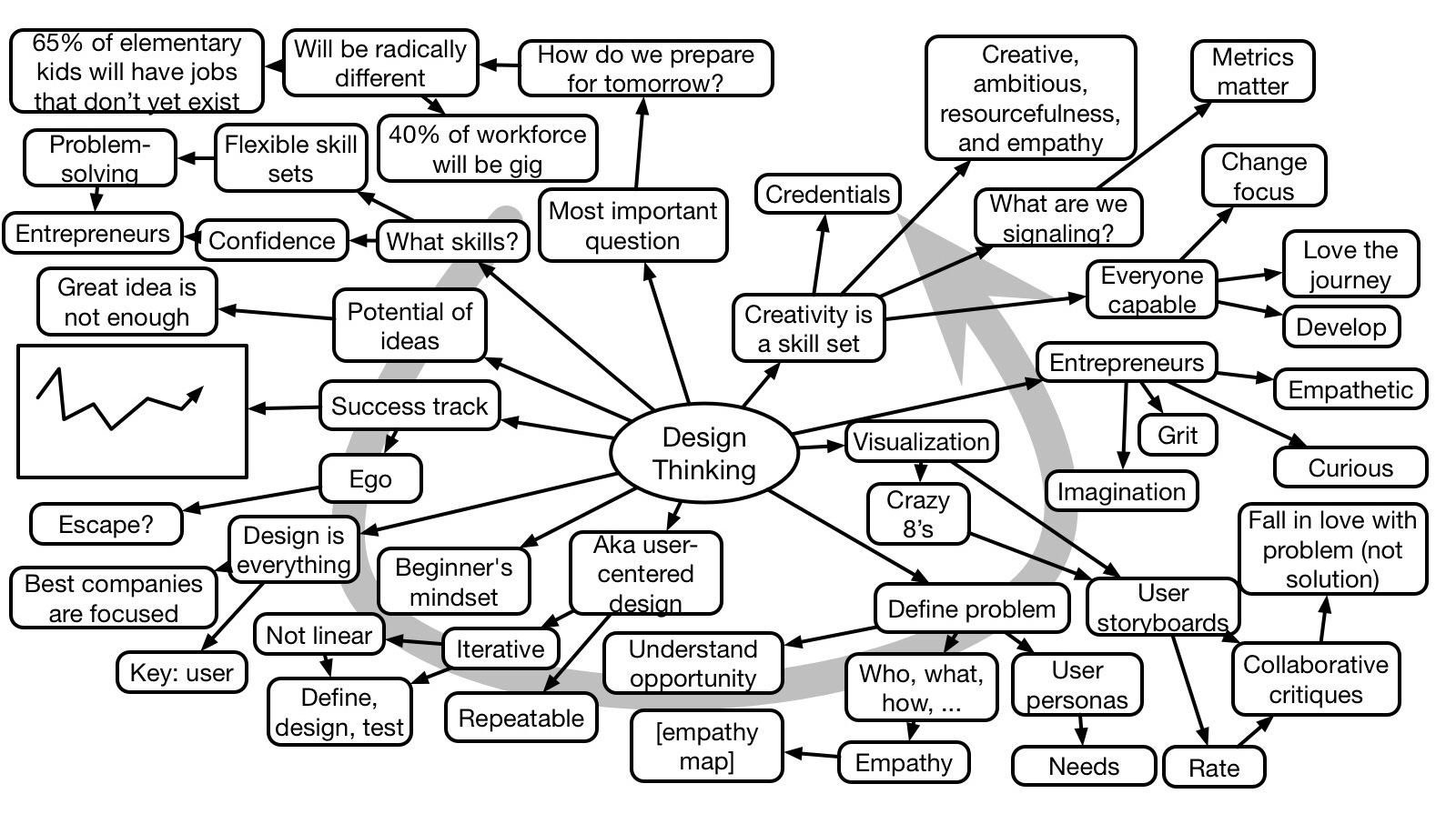
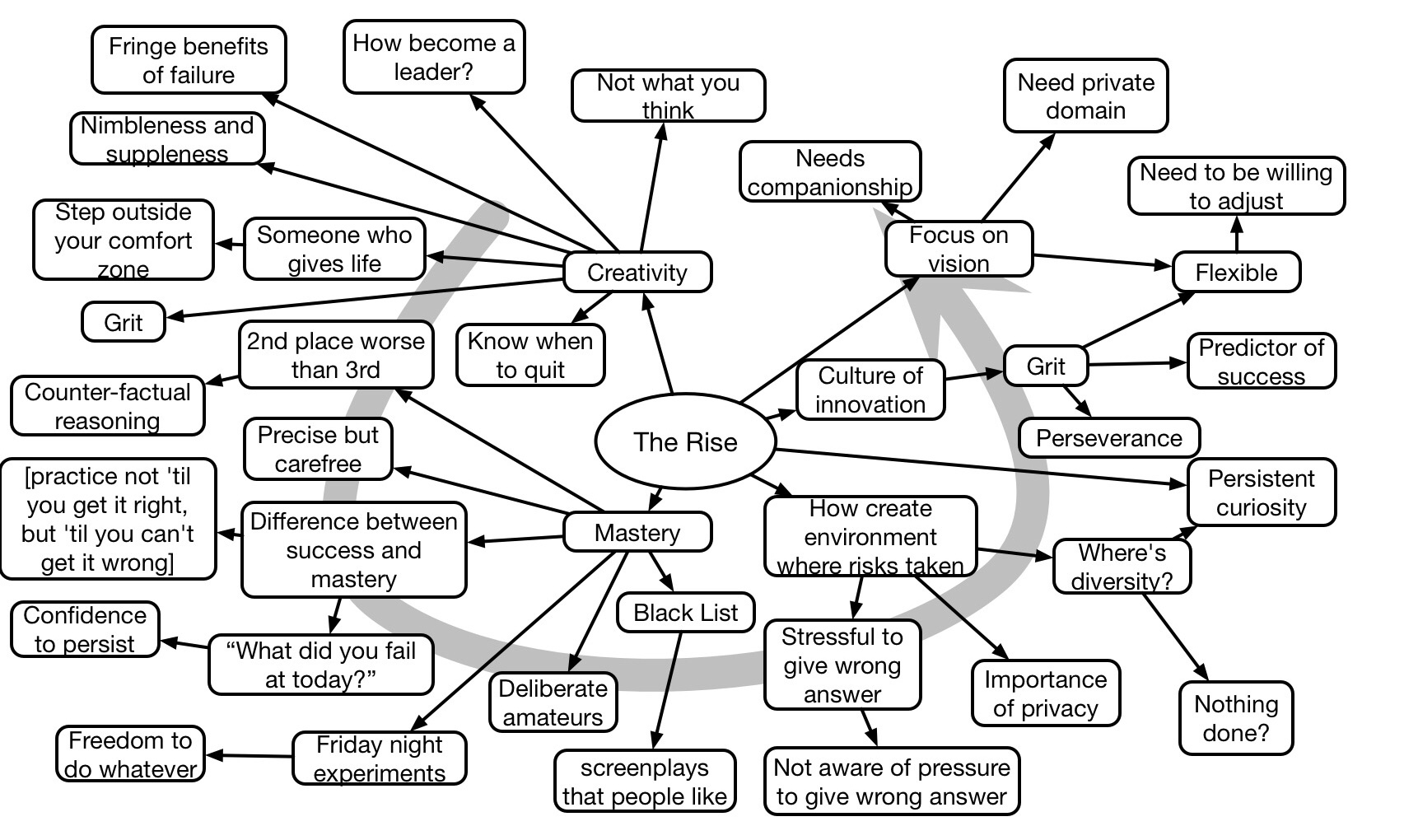
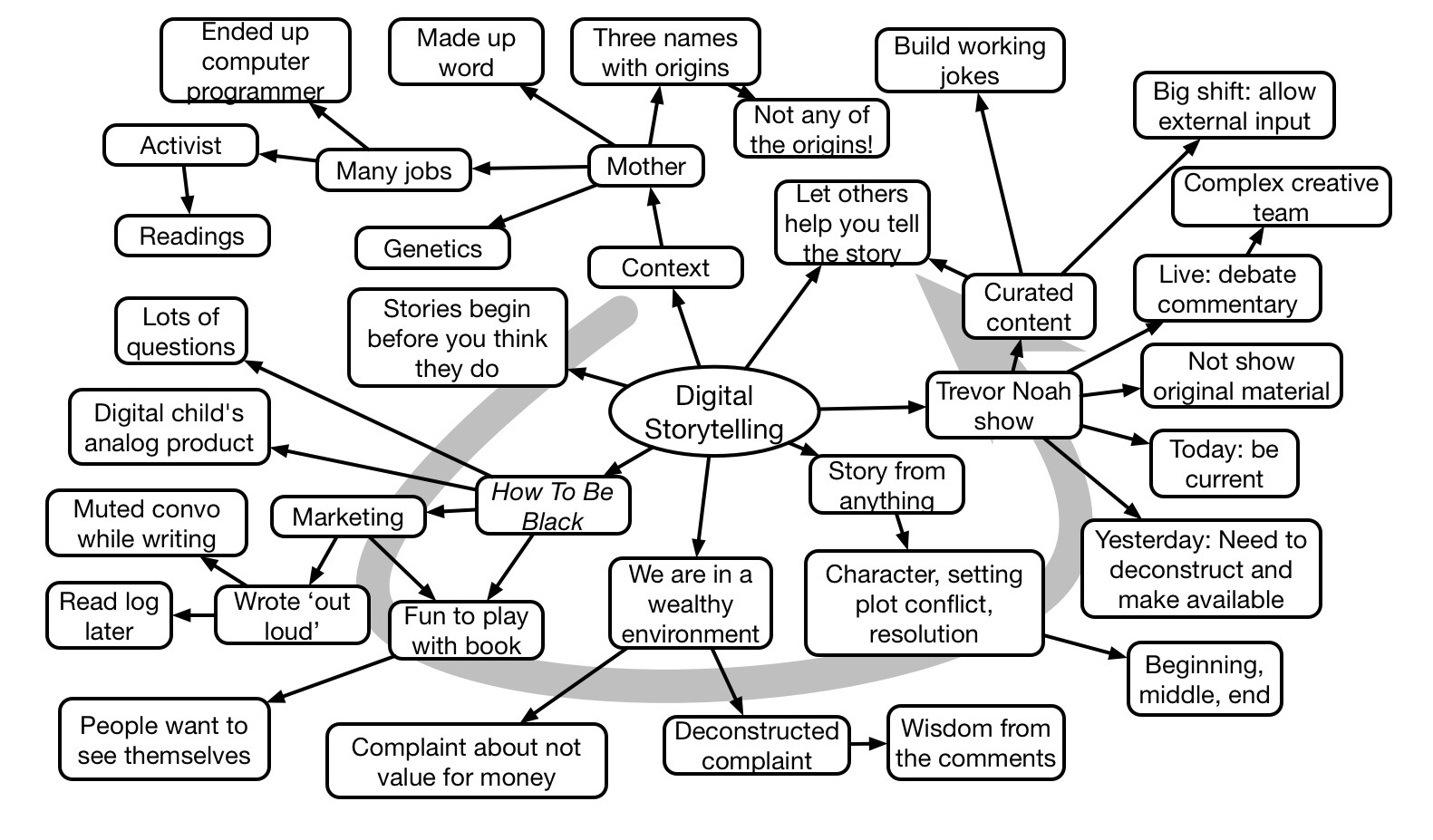
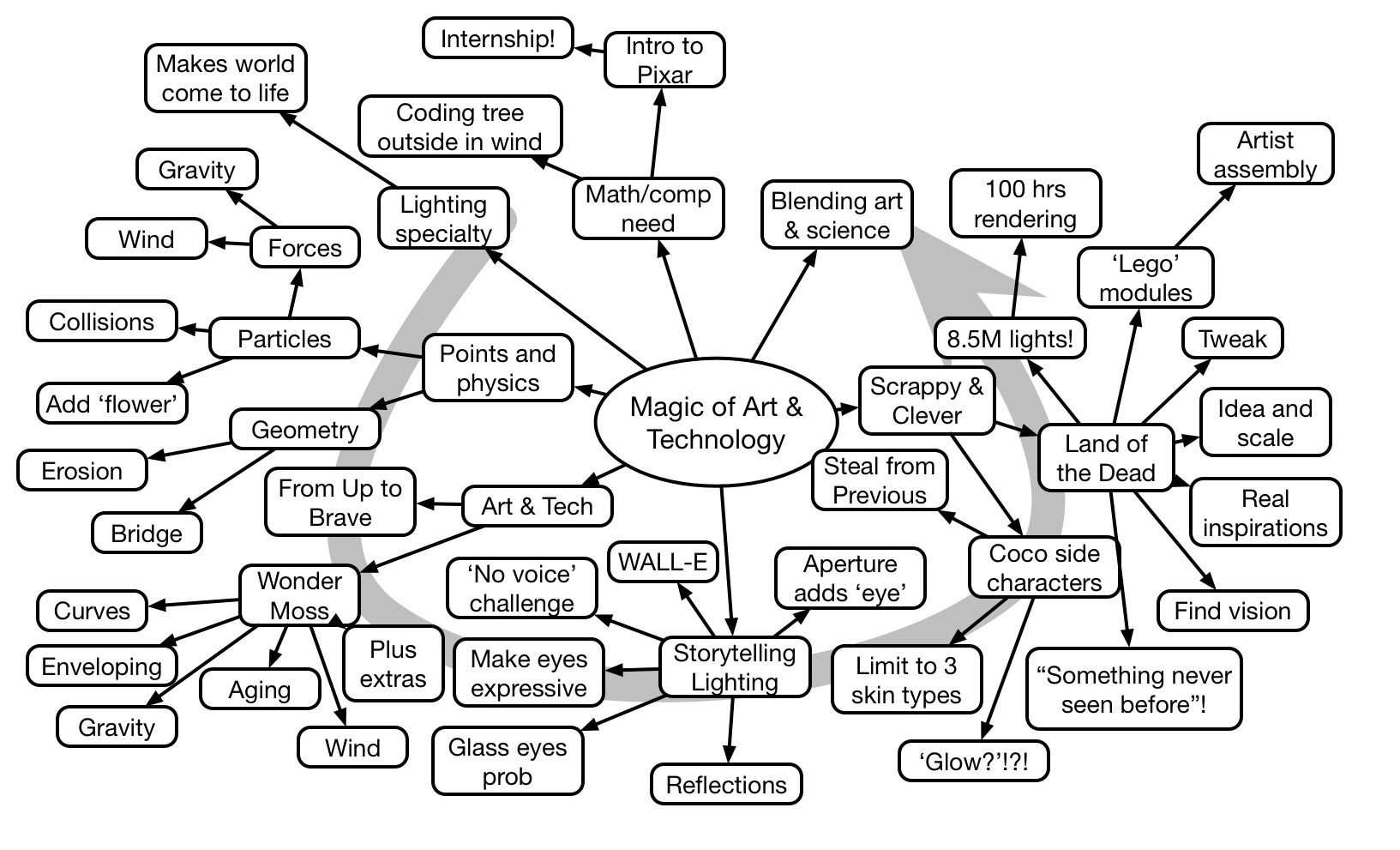
Sarah Prevette closed the Learning Solutions conference with a rapid fire overview of Design Thinking and a passionate case for making the success skills of the future to be entrepreneurship. Starting with her experiences, she laid out success factors, and suggested that these skills were learnable and should be the curriculum.